Welcome to the world of captive insurance, where businesses can unlock a plethora of benefits through strategic risk management. By delving into the realm of captive insurance, companies can gain more control over their risk exposure, potentially reducing costs and increasing financial stability. In this article, we will explore the key aspects of captive insurance, with a focus on the IRS 831(b) tax code and microcaptives. Prepare to navigate the intricate landscape of captive insurance and discover how it can be a game-changer for businesses seeking to optimize their risk management strategies. So, let’s dive in and uncover the potential advantages that lie within the captive insurance industry.
Understanding Captive Insurance
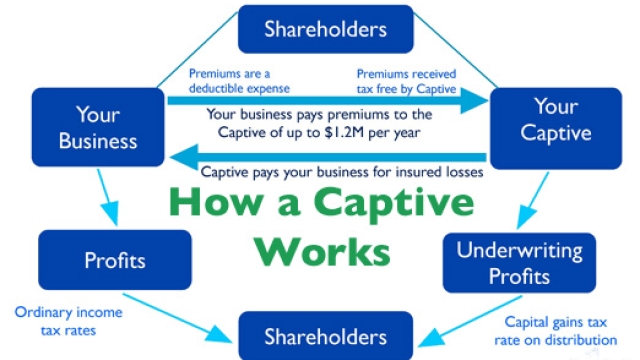
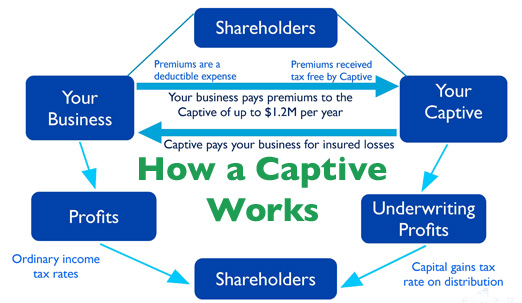
Captive insurance refers to a unique form of self-insurance that allows businesses to establish their own insurance company to cater specifically to their own risk management needs. This alternative approach offers several advantages to businesses, allowing them to have more control over their insurance coverage and potentially lower costs.
At the core, captive insurance involves a company creating its own insurance subsidiary, commonly referred to as a "captive." This captive then assumes the risks and provides insurance coverage for its parent company and affiliated entities. By having their own captive, businesses can tailor their insurance policies to address their specific risks and unique circumstances.
One popular category of captive insurance is the 831(b) microcaptive, named after the relevant section of the IRS tax code. Under this provision, captives with annual premiums below a certain threshold can elect to be taxed only on their investment income, rather than their underwriting income. This tax advantage has led to increased interest in microcaptives as a risk management strategy for small and mid-sized businesses.
By unlocking the benefits of captive insurance, businesses can gain more control over their risk management strategies and potentially achieve cost savings. With a captive in place, companies can customize their policies, claims processes, and risk management approaches to fit their unique needs. Moreover, the tax advantages provided by the 831b tax code add an additional layer of financial benefits for qualified captives.
Understanding the world of captive insurance is crucial for businesses looking to explore this alternative risk management solution. By delving into captive insurance options, such as the microcaptive model under the IRS 831(b) tax code, businesses can gain a competitive edge in managing their risks and protecting their assets.
The IRS 831(b) Tax Code
831b
In the realm of captive insurance, the IRS 831(b) tax code plays a significant role. It provides a beneficial opportunity for small and mid-sized businesses to form their captive insurance companies and enjoy tax advantages. Under this tax code, eligible captive insurance companies can elect to be taxed on their underwriting profits at a considerably lower rate.
One key requirement for qualifying under the IRS 831(b) tax code is that the captive insurance company’s annual premiums must not exceed $2.3 million. This threshold allows small and mid-sized businesses to harness the advantages of captive insurance without being overly burdened by high premium costs. By meeting this criterion, companies can gain greater control over their insurance coverage and potentially enhance their risk management strategies.
Microcaptives, which are a subset of captive insurance companies, can also take advantage of the IRS 831(b) tax code. These entities typically cater to companies with even smaller annual premiums. The code allows them to benefit from favorable tax treatment, providing an avenue to efficiently manage risks and address specific insurance needs.
The IRS 831(b) tax code serves as a catalyst for unlocking the potential benefits of captive insurance. It enables businesses to create tailored insurance programs, retain greater premiums, and obtain tax advantages. Understanding the intricacies of this tax code is essential for companies seeking to explore and leverage captive insurance to their advantage.
Benefits of Microcaptives
Microcaptives, also known as small captive insurance companies, offer numerous benefits to businesses that choose to establish them. These specialized insurance entities operate under the IRS 831(b) tax code and are gaining popularity due to the advantages they provide. Here are some key benefits of microcaptives:
Enhanced Risk Management:
By forming a microcaptive, businesses can gain greater control over their insurance coverage. They have the flexibility to customize policies to meet their specific risk management needs. Unlike traditional insurance providers, microcaptives allow policyholders to tailor coverage to their unique risks, providing a higher level of protection and reducing exposure to unforeseen events.
Potential Cost Savings:
One notable advantage of microcaptives is the potential for cost savings. Since premiums paid to a microcaptive are tax-deductible, businesses can effectively reduce their taxable income. This tax advantage can result in significant savings for companies, enabling them to allocate funds towards other business priorities or reinvest in their operations.
Wealth Accumulation and Wealth Transfer:
Microcaptives offer an avenue for wealth accumulation and wealth transfer. Through careful planning and the use of appropriate strategies, business owners can accumulate wealth within their microcaptive, which can then be accessed for future needs or wealth transfer purposes. This can provide stability to businesses and create long-term financial security.
In conclusion, microcaptives provide businesses with enhanced risk management capabilities, potential cost savings, and opportunities for wealth accumulation and transfer. As more companies explore captive insurance options, understanding the benefits of microcaptives can help them make informed decisions and leverage these advantages for their business growth.