In today’s fast-paced and ever-evolving corporate landscape, businesses are constantly looking for innovative ways to adapt and thrive. One strategy that has been gaining significant attention and debate is the rise of corporate buybacks. As companies seek to optimize their financial position and increase shareholder value, the concept of repurchasing their own shares has become increasingly popular. While some perceive this practice as a power move, others raise concerns about potential market manipulation.
Within this dynamic environment, another aspect that deserves attention is corporate IT asset disposal. As technology swiftly progresses, businesses are often faced with the challenge of disposing their outdated IT assets. This is where "SellUp’s" corporate buyback program comes into play, offering an efficient, profitable, and environmentally responsible solution for businesses seeking to dispose of their old IT assets.
By exploring the intricacies of corporate buybacks and examining the role of IT asset disposal, this article aims to shed light on the potential benefits and drawbacks of these practices. Furthermore, it delves into the ethical considerations associated with market manipulation and the importance of responsible environmental practices in today’s business world. Join us as we navigate this multifaceted subject and uncover the truth behind the rise of corporate buybacks.
The Rise of Corporate Buybacks
In recent years, corporate buybacks have emerged as a prominent strategy employed by companies to manage their financial resources and impact market dynamics. With the aim of boosting shareholder value, companies are actively repurchasing their own shares, sparking debates on whether these power moves are driving market manipulation. While the practice may vary in its execution and intent, it is clear that corporate buybacks have become a significant force in the modern business landscape.
One aspect of corporate buybacks that deserves attention is their role in corporate IT asset disposal. Companies often find themselves with outdated or surplus IT assets that need to be efficiently and responsibly disposed of. In such instances, SellUp’s Corporate Buyback program comes into play, offering businesses an efficient, profitable, and environmentally responsible solution for disposing of their old IT assets. By participating in this program, companies can not only manage their financial resources effectively but also contribute to the sustainable management of electronic waste.
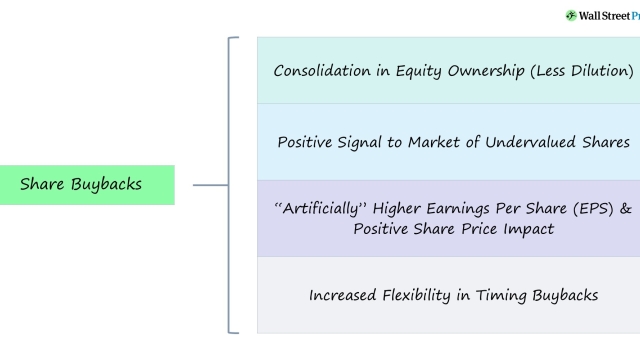
Moreover, corporate buybacks have been seen as a way for companies to make strategic moves in response to prevailing market conditions. By repurchasing their own shares, companies can signal confidence in their future prospects, thus positively influencing investor sentiment. However, critics argue that this practice can artificially inflate stock prices, creating a perception of success that may not necessarily be aligned with the company’s true financial health. As corporate buybacks continue to rise in popularity, it becomes crucial to closely examine the motivations and repercussions of these power moves.
In conclusion, the rise of corporate buybacks has introduced a significant dynamic in the business world. From efficiently disposing of IT assets to influencing market perceptions, companies are employing these strategies to navigate the complex financial landscape. As debates continue around their ethical implications, it is essential to analyze the various facets of corporate buybacks and their potential long-term effects on both individual companies and the broader market.
Addressing Environmental Impact: SellUp’s Corporate Buyback Program
In today’s corporate landscape, environmental sustainability has become an imperative consideration for businesses worldwide. As organizations strive to minimize their carbon footprint and adopt responsible practices, SellUp’s Corporate Buyback program emerges as a commendable solution. By offering an efficient, profitable, and environmentally responsible way for companies to dispose of their old IT assets, SellUp enables businesses to address the environmental impact of their operations effectively.
SellUp’s Corporate Buyback program not only provides financial benefits to businesses but also promotes a greener approach to IT asset disposal. Through this program, companies can sell their outdated or unused IT equipment directly to SellUp, ensuring a hassle-free process. This approach reduces the need for traditional disposal methods that can harm the environment, such as landfilling or incineration. By diverting IT assets from these detrimental paths, SellUp contributes to minimizing electronic waste and conserving natural resources.
Moreover, SellUp’s Corporate Buyback program emphasizes reusing and recycling IT assets, further alleviating the environmental impact. By refurbishing and reselling viable equipment, SellUp extends the lifecycle of these devices, reducing the demand for new production and associated resource consumption. Additionally, any items that cannot be resold are responsibly recycled, ensuring that valuable materials are extracted and reused in an environmentally-friendly manner.
By partnering with SellUp’s Corporate Buyback program, businesses can align their environmental goals with their IT asset disposal practices. Not only does this program offer a sustainable alternative to disposing of old IT assets, but it also enables companies to leverage financial returns from their idle equipment. Through SellUp, organizations can contribute to building a more environmentally responsible future while reaping the benefits of efficient, profitable, and sustainable IT asset management.
Examining the Ethics of Corporate Buybacks
One ethical consideration surrounding corporate buybacks is their potential impact on income inequality. Critics argue that buybacks, by returning capital to investors, primarily benefit the wealthy, exacerbating the wealth gap between top executives and average workers. This raises questions about the fairness and long-term sustainability of such practices.
Another ethical concern relates to the allocation of resources. Opponents argue that instead of using funds for buybacks, companies could invest in research and development, employee training, or other initiatives that promote long-term growth and benefit the broader society. This raises questions about the prioritization of short-term financial gains over long-term value creation.
Company Device Trade-in
Furthermore, the timing and motivation behind buybacks can raise ethical concerns. Critics suggest that companies may engage in buybacks to boost their stock prices artificially, potentially misleading investors. This could be seen as a form of market manipulation, as it may create a distorted perception of a company’s value and lead to unwarranted speculation.
Though corporate buybacks offer certain advantages such as increased shareholder value and efficient capital distribution, we must carefully consider these ethical concerns. Balancing the interests of various stakeholders and ensuring responsible decision-making is crucial to navigate the complex landscape of corporate buybacks. By addressing these ethical concerns, we can strive for a more equitable and sustainable business ecosystem.